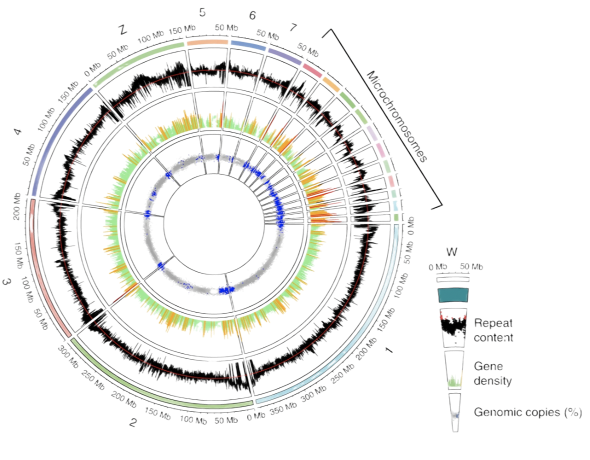
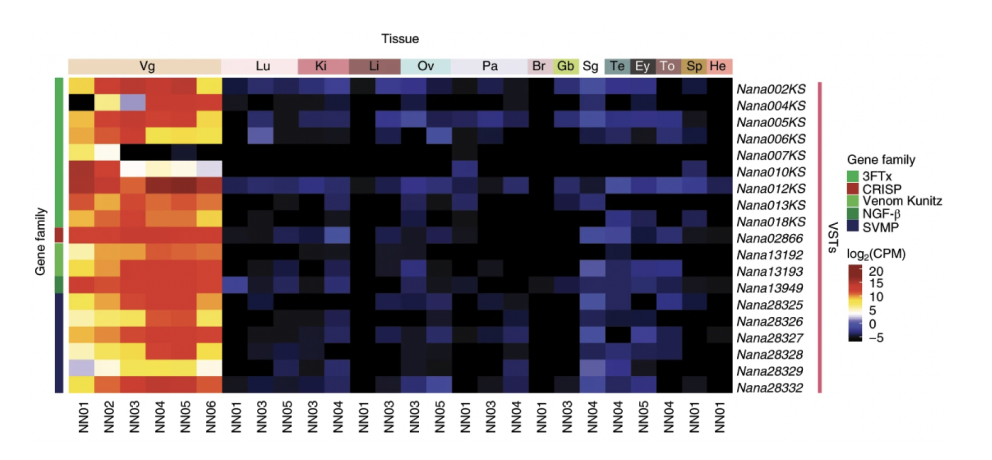
A comprehensive annotation pipeline identified 23,248 predicted protein-coding genes, of which 12,346 were venom-gland-expressed genes and constitute the ‘venom-ome.’ Venom gene-specific gene models were generated to identify 139 genes from 33 toxin families. This will aid in synthetic venom production through recombinant toxin expression and the rapid development of safe and effective synthetic antivenom. Additionally, this genome will serve as a reference for snake genomes, support evolutionary studies and enable venom-driven drug discovery.1
A
B
1. Suryamohan, K., et al. The Indian cobra reference genome and transcriptome enables comprehensive identification of venom toxins. Nat Genet 52, 106–117, 2020.